练习 1 分配并初始化一个进程控制块
static struct proc_struct *
alloc_proc(void) {
struct proc_struct *proc = kmalloc(sizeof(struct proc_struct));
if (proc != NULL) {
/*
* below fields in proc_struct need to be initialized
* enum proc_state state; // Process state
* int pid; // Process ID
* int runs; // the running times of Proces
* uintptr_t kstack; // Process kernel stack
* volatile bool need_resched; // bool value: need to be rescheduled to release CPU?
* struct proc_struct *parent; // the parent process
* struct mm_struct *mm; // Process's memory management field
* struct context context; // Switch here to run process
* struct trapframe *tf; // Trap frame for current interrupt
* uintptr_t cr3; // CR3 register: the base addr of Page Directroy * Table(PDT)
* uint32_t flags; // Process flag
* char name[PROC_NAME_LEN + 1]; // Process name
*/
proc->state = PROC_UNINIT;
proc->pid = -1;
proc->runs = 0;
proc->kstack = 0;
proc->need_resched = 0;
proc->parent = NULL;
proc->mm = NULL;
memset(&(proc->context), 0, sizeof(struct context));
proc->tf = NULL;
proc->cr3 = boot_cr3;
proc->flags = 0;
memset(proc->name, 0, PROC_NAME_LEN);
}
return proc;
}在 proc_alloc 中,需要做的只是找到一小块内存记录进程信息,然后用默认值初始化这块内存,因为一开始什么都没有确定,所以大部分默认值是 0,pid 则初始化为 -1 表示还没有分配 pid,state 初始化为 PROC_UNINIT 表示进程还没有被初始化,而页目录表地址则初始化为内核的页目录表,表示该线程在内核态中运行。这个函数只是相当于一个默认构造函数。
-
请说明
proc_struct中struct context context和struct trapframe *tf成员变量含义和在本实验中的作用是啥?// Saved registers for kernel context switches. // Don't need to save all the %fs etc. segment registers, // because they are constant across kernel contexts. // Save all the regular registers so we don't need to care // which are caller save, but not the return register %eax. // (Not saving %eax just simplifies the switching code.) // The layout of context must match code in switch.S. struct context { uint32_t eip; uint32_t esp; uint32_t ebx; uint32_t ecx; uint32_t edx; uint32_t esi; uint32_t edi; uint32_t ebp; };struct context中用于记录进程执行的上下文,也就是进程执行中的寄存器状态,在进程切换的时候会保存和恢复这些值。主要是在内核态切换到内核态的进程调度的时候使用。而
tf指向的是中断帧的指针,指向内核栈的某个位置,用来在进程执行中发生中断时保存中断现场用,例如在用户态中断到核心态的时候。
练习 2 为新创建的内核线程分配资源
int
do_fork(uint32_t clone_flags, uintptr_t stack, struct trapframe *tf) {
int ret = -E_NO_FREE_PROC;
struct proc_struct *proc;
if (nr_process >= MAX_PROCESS) {
goto fork_out;
}
ret = -E_NO_MEM;
// 1. call alloc_proc to allocate a proc_struct
proc = alloc_proc();
if (!proc) {
goto fork_out;
}
proc->parent = current;
// 2. call setup_kstack to allocate a kernel stack for child process
if (setup_kstack(proc) != 0) {
goto bad_fork_cleanup_kstack;
}
// 3. call copy_mm to dup OR share mm according clone_flag
if (copy_mm(clone_flags, proc) != 0) {
goto bad_fork_cleanup_kstack;
}
// 4. call copy_thread to setup tf & context in proc_struct
copy_thread(proc, stack, tf);
// 5. insert proc_struct into hash_list && proc_list
bool intr_flag;
local_intr_save(intr_flag);
proc->pid = get_pid();
list_add(&proc_list, &proc->list_link);
hash_proc(proc);
++nr_process;
local_intr_restore(intr_flag);
// 6. call wakeup_proc to make the new child process RUNNABLE
wakeup_proc(proc);
// 7. set ret vaule using child proc's pid
ret = proc->pid;
fork_out:
return ret;
bad_fork_cleanup_kstack:
put_kstack(proc);
bad_fork_cleanup_proc:
kfree(proc);
goto fork_out;
}在 alloc_proc 函数中,ucore 只是为 PCB 分配了一块内存并做了简单的初始化,所以创建内核线程的时候一般通过 do_fork 来分配一个新的进程并设置相关的资源。这个函数主要做以下操作:
- 调用
alloc_proc分配足够的内存给 PCB,并将新的proc的parent指针指向当前正在运行的进程。 - 调用
setup_kstack为子进程设置好内核栈。 - 调用
copy_mm将父进程的内存空间信息复制到子进程中,本实验暂时没有用到。 - 调用
copy_thread将父进程的上下文和栈复制到子进程中。 - 将该进程信息添加到进程列表中。
- 调用
wakeup_proc唤醒新进程。 - 将返回值设置为新进程的
pid。
-
请说明 ucore 是否做到给每个新
fork的线程一个唯一的 id?请说明你的分析和理由。查看
get_pid的函数定义:static int get_pid(void) { static_assert(MAX_PID > MAX_PROCESS); struct proc_struct *proc; list_entry_t *list = &proc_list, *le; static int next_safe = MAX_PID, last_pid = MAX_PID; if (++ last_pid >= MAX_PID) { last_pid = 1; goto inside; } if (last_pid >= next_safe) { inside: next_safe = MAX_PID; repeat: le = list; while ((le = list_next(le)) != list) { proc = le2proc(le, list_link); if (proc->pid == last_pid) { if (++ last_pid >= next_safe) { if (last_pid >= MAX_PID) { last_pid = 1; } next_safe = MAX_PID; goto repeat; } } else if (proc->pid > last_pid && next_safe > proc->pid) { next_safe = proc->pid; } } } return last_pid; }可以看到,这个函数在变量
last_pid中记录了最后一次分配的pid,而next_safe记录了pid的安全值。每次尝试获取新的pid的时候,就会先看看把最后一次分配的pid加 1 是不是安全的,如果不行,就遍历进程列表,确保新分配的pid是安全的。同时,在
do_fork调用get_pid的时候,会关闭中断,确保get_pid是原子操作,所以 ucore 做到了给每个新fork的线程一个唯一的 id。
练习 3 分析代码 proc_run 函数
void
proc_run(struct proc_struct *proc) {
if (proc != current) {
bool intr_flag;
struct proc_struct *prev = current, *next = proc;
local_intr_save(intr_flag);
{
current = proc;
load_esp0(next->kstack + KSTACKSIZE);
lcr3(next->cr3);
switch_to(&(prev->context), &(next->context));
}
local_intr_restore(intr_flag);
}
}proc_run 的作用是运行一个进程,如果要运行的进程和现在执行的一样,那就什么都不用做,否则的话,就把下一个要执行的进程的内核栈、页目录表加载进来,然后调用 switch_to 切换上下文。
switch_to 是一个汇编代码写的函数:
.text
.globl switch_to
switch_to: # switch_to(from, to)
# save from's registers
movl 4(%esp), %eax # eax points to from
popl 0(%eax) # save eip !popl
movl %esp, 4(%eax) # save esp::context of from
movl %ebx, 8(%eax) # save ebx::context of from
movl %ecx, 12(%eax) # save ecx::context of from
movl %edx, 16(%eax) # save edx::context of from
movl %esi, 20(%eax) # save esi::context of from
movl %edi, 24(%eax) # save edi::context of from
movl %ebp, 28(%eax) # save ebp::context of from
# restore to's registers
movl 4(%esp), %eax # not 8(%esp): popped return address already
# eax now points to to
movl 28(%eax), %ebp # restore ebp::context of to
movl 24(%eax), %edi # restore edi::context of to
movl 20(%eax), %esi # restore esi::context of to
movl 16(%eax), %edx # restore edx::context of to
movl 12(%eax), %ecx # restore ecx::context of to
movl 8(%eax), %ebx # restore ebx::context of to
movl 4(%eax), %esp # restore esp::context of to
pushl 0(%eax) # push eip
ret在调用这个函数的时候,栈的结构如下:
+| 栈底方向 | 高位地址
| to |
| from |
| 返回地址 | <-------- esp此时,from 在 esp + 4 处,存放指向 prev->context 的指针,然后按照 struct context 的结构依次保存现场,需要注意的是,在 popl 0(%eax) 之后,栈的结构变成了:
+| 栈底方向 | 高位地址
| to |
| from | <-------- esp所以,现在 esp + 4 处存放的就是 next->context 的指针了。此时读取 context 中的上下文,恢复进程的现场。
+| 栈底方向 | 高位地址
| to |
| from |
| 新进程 eip | <-------- esp最后,通过将 context 中的 eip 压栈,然后调用 ret 指令,使指令从新进程的现场继续执行。
在这次实验中,initproc 的 eip 在 copy_thread 中被设置成了 forkret:
static void
copy_thread(struct proc_struct *proc, uintptr_t esp, struct trapframe *tf) {
proc->tf = (struct trapframe *)(proc->kstack + KSTACKSIZE) - 1;
*(proc->tf) = *tf;
proc->tf->tf_regs.reg_eax = 0;
proc->tf->tf_esp = esp;
proc->tf->tf_eflags |= FL_IF;
proc->context.eip = (uintptr_t)forkret;
proc->context.esp = (uintptr_t)(proc->tf);
}-
在本实验的执行过程中,创建且运行了几个内核线程?
在
proc_init中,只有两个内核线程被创建:idleproc和initproc:void proc_init(void) { int i; list_init(&proc_list); for (i = 0; i < HASH_LIST_SIZE; i ++) { list_init(hash_list + i); } if ((idleproc = alloc_proc()) == NULL) { panic("cannot alloc idleproc.\n"); } idleproc->pid = 0; idleproc->state = PROC_RUNNABLE; idleproc->kstack = (uintptr_t)bootstack; idleproc->need_resched = 1; set_proc_name(idleproc, "idle"); nr_process ++; current = idleproc; int pid = kernel_thread(init_main, "Hello world!!", 0); if (pid <= 0) { panic("create init_main failed.\n"); } initproc = find_proc(pid); set_proc_name(initproc, "init"); assert(idleproc != NULL && idleproc->pid == 0); assert(initproc != NULL && initproc->pid == 1); }在其他初始化完成之后,ucore 就会调用
cpu_idle函数,这个函数是一个死循环,如果发现当前的内核线程让出了 CPU,就调用schedule函数进行进程调度。void schedule(void) { bool intr_flag; list_entry_t *le, *last; struct proc_struct *next = NULL; local_intr_save(intr_flag); { current->need_resched = 0; last = (current == idleproc) ? &proc_list : &(current->list_link); le = last; do { if ((le = list_next(le)) != &proc_list) { next = le2proc(le, list_link); if (next->state == PROC_RUNNABLE) { break; } } } while (le != last); if (next == NULL || next->state != PROC_RUNNABLE) { next = idleproc; } next->runs ++; if (next != current) { proc_run(next); } } local_intr_restore(intr_flag); }在这次实验里,一开始是
idleproc在运行,而且自己的resched置位,所以调度器会马上被唤醒,调度到initproc中,而在kernel_thread函数中,设置了initproc运行的参数:int kernel_thread(int (*fn)(void *), void *arg, uint32_t clone_flags) { struct trapframe tf; memset(&tf, 0, sizeof(struct trapframe)); tf.tf_cs = KERNEL_CS; tf.tf_ds = tf.tf_es = tf.tf_ss = KERNEL_DS; tf.tf_regs.reg_ebx = (uint32_t)fn; tf.tf_regs.reg_edx = (uint32_t)arg; tf.tf_eip = (uint32_t)kernel_thread_entry; return do_fork(clone_flags | CLONE_VM, 0, &tf); }initproc的中断栈帧的eip寄存器被设置成了kernel_thread_entry,ebx中保存着真正需要调用的函数地址,edx中保存着函数调用的参数。而在
do_fork的copy_thread函数中:static void copy_thread(struct proc_struct *proc, uintptr_t esp, struct trapframe *tf) { proc->tf = (struct trapframe *)(proc->kstack + KSTACKSIZE) - 1; *(proc->tf) = *tf; proc->tf->tf_regs.reg_eax = 0; proc->tf->tf_esp = esp; proc->tf->tf_eflags |= FL_IF; proc->context.eip = (uintptr_t)forkret; proc->context.esp = (uintptr_t)(proc->tf); }可以看到内核线程的真正入口地址是
forkret,所以在switch_to调用之后,会跳转到forkret:static void forkret(void) { forkrets(current->tf); }这是所有新进程的入口地址,
forkrets是汇编函数:.globl __trapret __trapret: # restore registers from stack popal # restore %ds, %es, %fs and %gs popl %gs popl %fs popl %es popl %ds # get rid of the trap number and error code addl $0x8, %esp iret .globl forkrets forkrets: # set stack to this new process's trapframe movl 4(%esp), %esp jmp __trapret这里简单地将之前设置的
trapframe的值写入到寄存器中,并调用iret返回(因为只有iret可以修改段寄存器的值),而此时就会进入kernel_thread_entry:.text .globl kernel_thread_entry kernel_thread_entry: # void kernel_thread(void) pushl %edx # push arg call *%ebx # call fn pushl %eax # save the return value of fn(arg) call do_exit # call do_exit to terminate current thread这里就是调用线程函数,
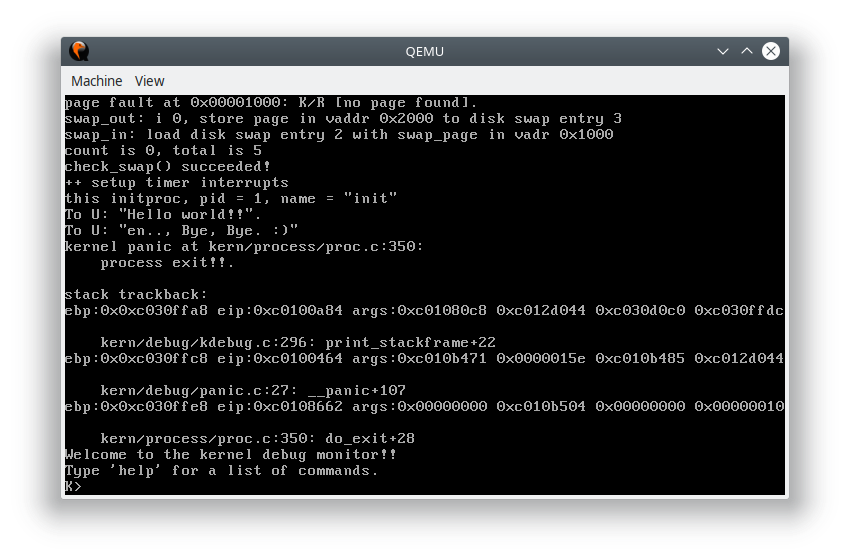
fn(arg),将返回值保存到栈上,最后调用do_exit退出进程:int do_exit(int error_code) { panic("process exit!!.\n"); }实验执行到这里就结束了。
-
语句
local_intr_save(intr_flag); ...; local_intr_restore(intr_flag);在这里有何作用?请说明理由。在准备切换进程的时候,需要重新设置栈和页表,并且需要切换进程上下文,如果不关中断,进程信息设置到一半的时候很可能会被中断打断,导致寄存器状态处于一个不一致的状态,造成程序运行出错。
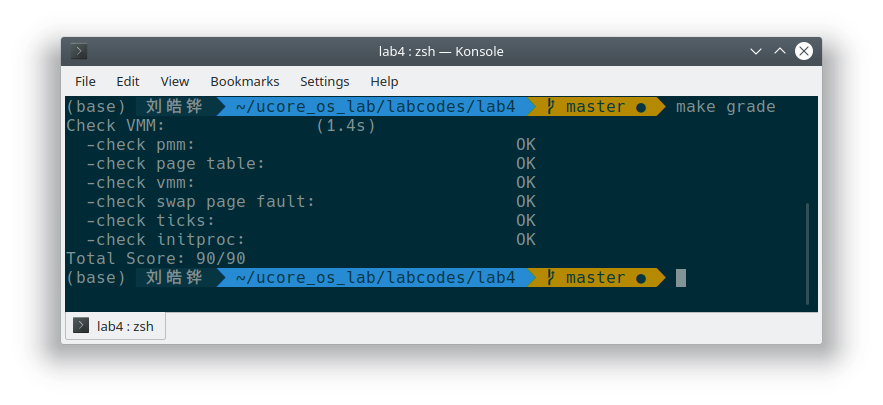
运行结果